February 27, 2022
Customers who own or manage an Autonomous System (AS) cloud enjoy the benefit from using Nexusguard Cloud Diversion (aka. Off-Net) to protect the whole IP subnet, as introduced in our Cloud Diversion Blog post. Triggered when traffic levels exceed a predefined threshold, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) route announcement of the under attack /24 IP prefix is advertised by Nexusguard Cloud to the Internet via the Cloud Diversion App, diverting customer’s traffic to our scrubbing centres for cleaning. After the scrubbing process, legitimate traffic is returned to the customer network via a pre-built GRE tunnel.
Nexusguard Off-Net vs On-Net
For Off-Net to function optimally, a certain degree of human intervention is required to stop announcements from being advertised to the Internet in the wake of an attack. In peacetime, regular announcements are made to both the Internet and the Nexusguard Cloud. When an attack is imminent, however, the Cloud Diversion agent issues a traffic diversion signal to the Nexusguard Cloud requesting an attack time announcement be made to the Internet. During the attack event, customers are then required to manually withdraw all regular announcements to the Internet so as to ensure that attack traffic is prevented from entering the upstream path.
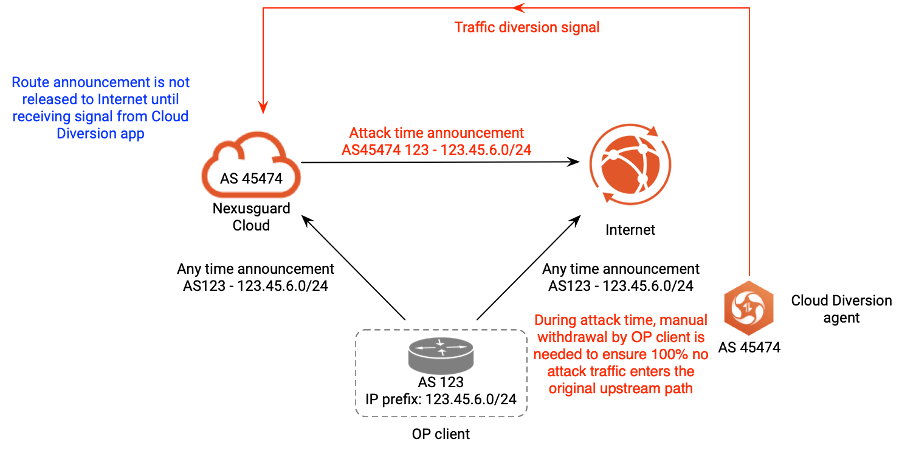
Figure 1 - Nexusguard Off-Net method
On-Net is Nexusguard’s enhanced version of Off-Net - the main difference between these two methods lie in their routing arrangements. In the Off-Net method, the Cloud Diversion agent is linked to the routing domain of the Nexusguard Cloud. However, with On-Net, the Cloud Diversion agent joins the routing domain of the Customer, allowing the agent to communicate with and share routing information with the Customer Router within the same ASN, facilitating decision-making and expediting time-to-mitigation. Peering takes place between the Cloud Diversion agent and the Customer Router since they are configured as internal peers within the Customer Routing domain, sharing the same routing policies.
BGP Community is a numerical value that is essentially a label or tag used to assist the Customer Router in identifying the IP prefix under attack, such that when the peer router receives the route announcement, it examines the community value prior to making the route decision. In peacetime, the Customer Router makes announcements directly to the Internet, while announcements to the Nexusguard Cloud, as confirmed by the “attack” BGP community, are issued only during attack time, thereby allowing attack mitigation to take effect immediately.
The automated mitigation process can be broken down as follows:
1. Cloud Diversion agent sends a signal to the Customer Router informing it of an impending attack
2. Customer Router, based on the “attack” BGP community value, makes the decision to simultaneously issue attack time announcements to Nexusguard Cloud and withdraw peacetime announcements from the original uplink to the Internet.
3. Nexusguard Cloud issues attack time announcement to Internet
 Figure 2 - Nexusguard’s enhanced cloud diversion method, On-Net
Figure 2 - Nexusguard’s enhanced cloud diversion method, On-Net
Solution Benefits of On-Net
With Nexusguard’s enhanced On-Net, customer traffic can be effortlessly and automatically diverted to the Nexusguard Cloud when anomalies occur, so that attack mitigation can take place effectively, ensuring only legitimate traffic enters customer networks at all times.
On-Net’s automated routing arrangement between Cloud Diversion agent and Customer Router not only minimizes latency brought about by the manual update process in the Off-Net method, but also drastically improves time-to-mitigation, ensuring customer assets are always protected, even during an attack.
On-Net is available to customers using our Origin Protection service. For further information, please read about Nexusguard’s Origin Protection.


